The tidiness of elementary mathematics: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(→The awkward integral when k=-1) |
|||
| (5 dazwischenliegende Versionen von einem Benutzer werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 10: | ||
== Main article == | == Main article == | ||
| − | + | Exceptional cases such as this are particularly problematic when we attempt to automate knowledge, that is when we seek to devise a ''computer algebra system'' which will symbolically manipulate expressions. If we want to integrate <math>x^{k}</math> with respect to <math>x</math> we certainly have two choices | |
# Ignore the special case <math>k=-1</math>. | # Ignore the special case <math>k=-1</math>. | ||
# Ask the user if <math>k=-1</math>. | # Ask the user if <math>k=-1</math>. | ||
| − | Both of these approaches are problematic. <math>k=-1</math> is only one point out of an infinity of other values for <math>k</math>. However, in mathematics such exceptional cases occur rather more often than you might expect if you just stuck a pin in the number line, or even if you chose an integer <math>k</math> at random. Asking the user can also be problematic as they many not yet know the value of <math>k</math>, or the integral might occur deep within some other function and the user may have no idea what the question is asking! Automatically using the formula might result in an error creeping into a much longer calculation. Mistakes like this are very hard to track down and can be serious. | + | Both of these approaches are problematic. <math>k=-1</math> is only one point out of an infinity of other values for <math>k</math>. However, in mathematics such exceptional cases occur rather more often than you might expect if you just stuck a pin in the number line, or even if you chose an integer <math>k</math> at random. Asking the user can also be problematic as they many not yet know the value of <math>k</math>, or the integral might occur deep within some other function and the user may have no idea what the question is asking! Automatically using the formula might result in an error creeping into a much longer calculation. Mistakes like this are very hard to track down and can be serious. These issues are addressed more fully by [2]. |
| − | What we would really like is a formula that works for all <math>k</math>. Here we are going to consider the comment in | + | What we would really like is a formula that works for all <math>k</math>. Here we are going to consider the comment in [2] that really, at a symbolic level, the answer to <math>\int x^k\mathrm{d}x </math> might better be written as <math> |
\int x^k\mathrm{d}x = \frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}+c. | \int x^k\mathrm{d}x = \frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}+c. | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| Zeile 23: | Zeile 23: | ||
First consider the (easy) case <math>k\neq -1</math>. If we fix <math>k</math> and differentiate then we obtain <math>\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}x}\frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1} = x^k.</math> So <math>\frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}=\frac{x^{k+1}}{k+1}-\frac{1}{k+1}</math> is an anti-derivative of <math>x^k</math>. Really we have chosen a slightly different constant of integration. | First consider the (easy) case <math>k\neq -1</math>. If we fix <math>k</math> and differentiate then we obtain <math>\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}x}\frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1} = x^k.</math> So <math>\frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}=\frac{x^{k+1}}{k+1}-\frac{1}{k+1}</math> is an anti-derivative of <math>x^k</math>. Really we have chosen a slightly different constant of integration. | ||
| − | Whereas we originally had the form <math>\frac{x^{0}}{0}=\frac{1}{0}</math>, the new formula gives <math>\frac{x^{0}-1}{0}=\frac{0}{0}</math>. To understand what is going on we need to look at this expression for <math>k</math> close to <math>-1</math> and take a limit, i.e. <math>\lim_{k\rightarrow -1} \frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}.</math> If we can make sense of this limit, then we will define the value of the expression at <math>k=-1</math> by the value of the limit, thus removing the exceptional case in a meaningful way. This sort of thing is a standard mathematician’s move. | + | Whereas, for <math>k=-1</math> we originally had the form <math>\frac{x^{0}}{0}=\frac{1}{0}</math>, the new formula gives <math>\frac{x^{0}-1}{0}=\frac{0}{0}</math>. To understand what is going on we need to look at this expression for <math>k</math> close to <math>-1</math> and take a limit, i.e. <math>\lim_{k\rightarrow -1} \frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}.</math> If we can make sense of this limit, then we will define the value of the expression at <math>k=-1</math> by the value of the limit, thus removing the exceptional case in a meaningful way. This sort of thing is a standard mathematician’s move. |
= Euler’s formula for <math>e^x = \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty} \left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n</math> = | = Euler’s formula for <math>e^x = \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty} \left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n</math> = | ||
| − | To consider the special case <math>k=-1</math> we shall need to make use of a special formula discovered by Euler. | + | To consider the special case <math>k=-1</math> we shall need to make use of a special formula discovered by Euler. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | On the right, we can expand out the product using the Binomial Theorem <math>\left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n | + | <math> e^x = \lim_{n\rightarrow\infty} \left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | If we consider the Taylor series for <math>e^x</math>, on the left hand side we have | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>e^x = 1+x+\frac{x^2}{2!}+\frac{x^3}{3!}+\frac{x^4}{4!}+\cdots </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | On the right, we can expand out the product using the Binomial Theorem | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n | ||
= \sum_{i=0}^n \frac{n(n-1)\cdots(n-i+1)}{i!}\left(\frac{x}{n}\right)^i | = \sum_{i=0}^n \frac{n(n-1)\cdots(n-i+1)}{i!}\left(\frac{x}{n}\right)^i | ||
| − | = \sum_{i=0}^n \frac{x^i}{i!} \frac{n(n-1)\cdots(n-i+1)}{n^i}.</math> Consider the coefficients of <math>x^i</math>. This equals <math>\frac{1}{i!} \frac{n(n-1)\cdots(n-i+1)}{n^i} = \frac{1}{i!} \frac{n}{n}\frac{n-1}{n} \cdots \frac{n-i+1}{n}.</math> As <math>n\rightarrow \infty</math> each term here containing <math>n</math> converges to <math>1</math> giving <math>\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty} \left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n = \sum_{i=0}^\infty \frac{x^i}{i!},</math> or exactly the Taylor series for <math>e^x</math>. | + | = \sum_{i=0}^n \frac{x^i}{i!} \frac{n(n-1)\cdots(n-i+1)}{n^i}.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | Consider the coefficients of <math>x^i</math>. This equals <math>\frac{1}{i!} \frac{n(n-1)\cdots(n-i+1)}{n^i} = \frac{1}{i!} \frac{n}{n}\frac{n-1}{n} \cdots \frac{n-i+1}{n}.</math> As <math>n\rightarrow \infty</math> each term here containing <math>n</math> converges to <math>1</math> giving <math>\lim_{n\rightarrow\infty} \left( 1+\frac{x}{n}\right)^n = \sum_{i=0}^\infty \frac{x^i}{i!},</math> or exactly the Taylor series for <math>e^x</math>. | ||
You might think this argument has made somewhat cavalier use of limits. The following argument, adapted from [1], is close to Euler’s original. He was even more bold in his use of limits! | You might think this argument has made somewhat cavalier use of limits. The following argument, adapted from [1], is close to Euler’s original. He was even more bold in his use of limits! | ||
| Zeile 40: | Zeile 48: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
Thinking about <math>e^x</math> near <math>x=0</math>, and its gradient, we see that, for infinitely small <math>\epsilon</math> <math>e^\epsilon = 1 + \epsilon | Thinking about <math>e^x</math> near <math>x=0</math>, and its gradient, we see that, for infinitely small <math>\epsilon</math> <math>e^\epsilon = 1 + \epsilon | ||
| − | </math> | + | </math> Let <math>x</math> be any given number then <math>N=x/\epsilon</math> is infinitely large. So <math>e^x = e^{N\epsilon} = (e^\epsilon)^N |
= (1+\epsilon)^N | = (1+\epsilon)^N | ||
= \left( 1 +\frac{x}{N} \right)^N. | = \left( 1 +\frac{x}{N} \right)^N. | ||
| Zeile 51: | Zeile 59: | ||
= The awkward integral when <math>k=-1</math> = | = The awkward integral when <math>k=-1</math> = | ||
| − | We shall make use of Euler’s limit to evaluate the awkward integral when <math>k=-1</math>. <math> | + | We shall make use of Euler’s limit to evaluate the awkward integral when <math>k=-1</math>. |
| − | + | ||
| − | </math> Rearranging this we have <math>x^{\frac{1}{n}} = 1 + \frac{y}{n}</math> and then <math>y = n \left(x^{\frac{1}{n}} -1\right).</math> Let <math>m=\frac{1}{n}</math> so <math>y = \frac{1}{m} \left(x^{m}-1\right)=\frac{x^m-1}{m}.</math> Now, set <math>m=k+1</math>, to give <math>y =\frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}</math> and we are coming somewhat closer to the right hand side of . | + | Let <math> x = \left( 1+\frac{y}{n}\right)^n.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | Rearranging this we have <math>x^{\frac{1}{n}} = 1 + \frac{y}{n}</math> and then <math>y = n \left(x^{\frac{1}{n}} -1\right).</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>m=\frac{1}{n}</math> so <math>y = \frac{1}{m} \left(x^{m}-1\right)=\frac{x^m-1}{m}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now, set <math>m=k+1</math>, to give <math>y =\frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1}</math> and we are coming somewhat closer to the right hand side of the formula for our integral. | ||
If <math>k\rightarrow -1</math>, then <math>m\rightarrow 0</math> and <math>n=\frac{1}{m}\rightarrow \infty</math>. But if <math>n\rightarrow \infty</math> then we may apply to and conclude that <math>x=e^y</math>. Taking the inverse gives <math>y=\ln(x)</math>. Hence <math>\lim_{k\rightarrow -1} \frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1} = \ln(x)</math> and so is indeed valid for all <math>k</math>, including the special case <math>k=-1</math>, when we define the value of in this case by the limit <math>\lim_{k\rightarrow -1}</math>. This limit happens to give the right answer to the integral for <math>k=-1</math>. | If <math>k\rightarrow -1</math>, then <math>m\rightarrow 0</math> and <math>n=\frac{1}{m}\rightarrow \infty</math>. But if <math>n\rightarrow \infty</math> then we may apply to and conclude that <math>x=e^y</math>. Taking the inverse gives <math>y=\ln(x)</math>. Hence <math>\lim_{k\rightarrow -1} \frac{x^{k+1}-1}{k+1} = \ln(x)</math> and so is indeed valid for all <math>k</math>, including the special case <math>k=-1</math>, when we define the value of in this case by the limit <math>\lim_{k\rightarrow -1}</math>. This limit happens to give the right answer to the integral for <math>k=-1</math>. | ||
| Zeile 67: | Zeile 81: | ||
There is a deep consistency to elementary mathematics, sometimes we just have to search to find it. | There is a deep consistency to elementary mathematics, sometimes we just have to search to find it. | ||
| − | + | = References = | |
| + | |||
| + | [1] C. H. Edwards. The Historical Development of the Calculus. Springer-Verlag, 1979. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [2] D. R. Stoutemyer. Crimes and misdemeanors in the computer algebra trade. Notices of the American Mathematical Society, 38(7):778-785, September 1991. | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 11. November 2011, 00:04 Uhr
We all expect a certain tidiness to mathematics, and for many this provides a gratifying aesthetic pleasure. However, there are some wrinkles. One of these arises in the integral of 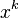 . Calculus provides us with the formula
. Calculus provides us with the formula 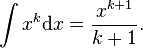 However, this equation is only correct for
However, this equation is only correct for 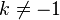 . If we try to take
. If we try to take 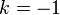 the right hand side is meaningless because we have a zero on the denominator of the fraction, i.e.
the right hand side is meaningless because we have a zero on the denominator of the fraction, i.e.  . But in this case a separate argument gives the answer
. But in this case a separate argument gives the answer 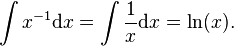
Our expectation is that these two formulae should be reconciled. Indeed, if we let 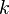 approach
approach 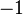 in the first we should end up with the second, but that fails to happen. For each
in the first we should end up with the second, but that fails to happen. For each 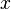 ,
, 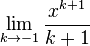 is undefined.
is undefined.
This vingette explores this issue.
Inhaltsverzeichnis |
Main article
Exceptional cases such as this are particularly problematic when we attempt to automate knowledge, that is when we seek to devise a computer algebra system which will symbolically manipulate expressions. If we want to integrate 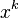 with respect to
with respect to 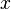 we certainly have two choices
we certainly have two choices
- Ignore the special case
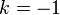 .
.
- Ask the user if
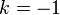 .
.
Both of these approaches are problematic. 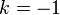 is only one point out of an infinity of other values for
is only one point out of an infinity of other values for 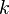 . However, in mathematics such exceptional cases occur rather more often than you might expect if you just stuck a pin in the number line, or even if you chose an integer
. However, in mathematics such exceptional cases occur rather more often than you might expect if you just stuck a pin in the number line, or even if you chose an integer 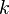 at random. Asking the user can also be problematic as they many not yet know the value of
at random. Asking the user can also be problematic as they many not yet know the value of 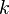 , or the integral might occur deep within some other function and the user may have no idea what the question is asking! Automatically using the formula might result in an error creeping into a much longer calculation. Mistakes like this are very hard to track down and can be serious. These issues are addressed more fully by [2].
, or the integral might occur deep within some other function and the user may have no idea what the question is asking! Automatically using the formula might result in an error creeping into a much longer calculation. Mistakes like this are very hard to track down and can be serious. These issues are addressed more fully by [2].
What we would really like is a formula that works for all 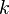 . Here we are going to consider the comment in [2] that really, at a symbolic level, the answer to
. Here we are going to consider the comment in [2] that really, at a symbolic level, the answer to 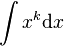 might better be written as
might better be written as 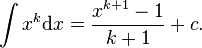
First consider the (easy) case 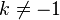 . If we fix
. If we fix 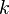 and differentiate then we obtain
and differentiate then we obtain 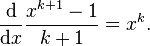 So
So 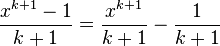 is an anti-derivative of
is an anti-derivative of 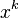 . Really we have chosen a slightly different constant of integration.
. Really we have chosen a slightly different constant of integration.
Whereas, for 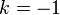 we originally had the form
we originally had the form 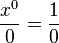 , the new formula gives
, the new formula gives 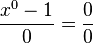 . To understand what is going on we need to look at this expression for
. To understand what is going on we need to look at this expression for 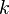 close to
close to 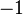 and take a limit, i.e.
and take a limit, i.e. 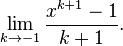 If we can make sense of this limit, then we will define the value of the expression at
If we can make sense of this limit, then we will define the value of the expression at 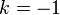 by the value of the limit, thus removing the exceptional case in a meaningful way. This sort of thing is a standard mathematician’s move.
by the value of the limit, thus removing the exceptional case in a meaningful way. This sort of thing is a standard mathematician’s move.
Euler’s formula for 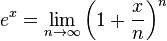
To consider the special case 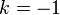 we shall need to make use of a special formula discovered by Euler.
we shall need to make use of a special formula discovered by Euler.
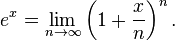
If we consider the Taylor series for 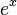 , on the left hand side we have
, on the left hand side we have
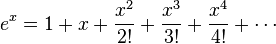
On the right, we can expand out the product using the Binomial Theorem
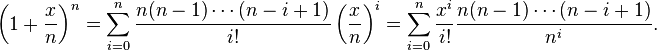
Consider the coefficients of 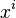 . This equals
. This equals 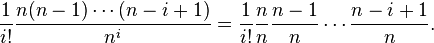 As
As 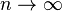 each term here containing
each term here containing 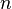 converges to
converges to 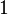 giving
giving 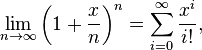 or exactly the Taylor series for
or exactly the Taylor series for 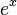 .
.
You might think this argument has made somewhat cavalier use of limits. The following argument, adapted from [1], is close to Euler’s original. He was even more bold in his use of limits!
Euler unhesitatingly accepts the existence of both infinitely small and infinitely large numbers, and uses them to such effect that the modern reader’s own hesitation must be tinged with envy. [1]
Thinking about 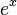 near
near 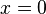 , and its gradient, we see that, for infinitely small
, and its gradient, we see that, for infinitely small 
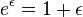 Let
Let 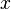 be any given number then
be any given number then 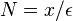 is infinitely large. So
is infinitely large. So 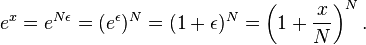 Written in terms of limits, the infinitely large
Written in terms of limits, the infinitely large 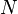 would give us our formula.
would give us our formula.
In this applet move the slider so that 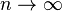 .
.
The awkward integral when 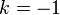
We shall make use of Euler’s limit to evaluate the awkward integral when 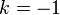 .
.
Let 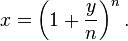
Rearranging this we have 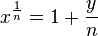 and then
and then 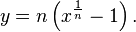
Let 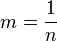 so
so 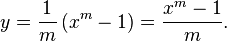
Now, set 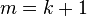 , to give
, to give 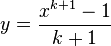 and we are coming somewhat closer to the right hand side of the formula for our integral.
and we are coming somewhat closer to the right hand side of the formula for our integral.
If 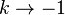 , then
, then 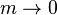 and
and 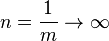 . But if
. But if 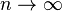 then we may apply to and conclude that
then we may apply to and conclude that 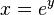 . Taking the inverse gives
. Taking the inverse gives 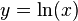 . Hence
. Hence 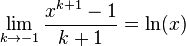 and so is indeed valid for all
and so is indeed valid for all 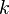 , including the special case
, including the special case 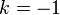 , when we define the value of in this case by the limit
, when we define the value of in this case by the limit 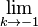 . This limit happens to give the right answer to the integral for
. This limit happens to give the right answer to the integral for 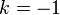 .
.
We can see this limit in the applet below. Mve the slider so that 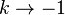 .
.
The mathematical moral
They key to all of this is to choose the constant of integration in so that the resulting formula also holds in the awkward limiting case, 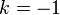 . Like many tricks in mathematics it is a technique which occasionally has useful applications elsewhere.
. Like many tricks in mathematics it is a technique which occasionally has useful applications elsewhere.
There is a deep consistency to elementary mathematics, sometimes we just have to search to find it.
References
[1] C. H. Edwards. The Historical Development of the Calculus. Springer-Verlag, 1979.
[2] D. R. Stoutemyer. Crimes and misdemeanors in the computer algebra trade. Notices of the American Mathematical Society, 38(7):778-785, September 1991.
