Algebra: Gleichungen: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus DMUW-Wiki
K |
K |
||
| (2 dazwischenliegende Versionen von einem Benutzer werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| − | < | + | <div style="border: 3px solid #551A8B ; background-color:#CD96CD ; padding:7px;"><big><span style="color:#551A8B ">'''Gleichungen</span>'''</big></div> |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | </ | + | |
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Zeile 13: | Zeile 11: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | <span style="background:#CD96CD ">'''Deine neue Lieblings-Merkregel zum Umformen von Termen und Gleichungen:'''</span><br> | |
| + | <div class="schuettel-quiz"> | ||
| + | Rechne immer '''Klammer''' vor '''Punkt''' vor '''Strich'''! | ||
| + | </div> | ||
<span style="background:#CD96CD ">'''Wende diese Regel nun auf die folgenden Aufgaben an. Beachte immer die Grundmenge, die rechts steht.'''</span> | <span style="background:#CD96CD ">'''Wende diese Regel nun auf die folgenden Aufgaben an. Beachte immer die Grundmenge, die rechts steht.'''</span> | ||
| Zeile 154: | Zeile 155: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | * <math> | + | * -3 <math>\cdot</math>(3 - 2x) + 2x = -21 |
<div align="right"><math>\mathbb{G}=\mathbb{Q}</math></div> | <div align="right"><math>\mathbb{G}=\mathbb{Q}</math></div> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 17. Juli 2009, 14:17 Uhr
Gleichungen
|
Wie bei einer Waage müssen beide Seiten der Gleichung immer im Gleichgewicht sein. Dies erreichst du durch Äquivalenzumformungen, mit denen du beide Seiten der Gleichung einheitlich umstellst, ohne dass sich der Wert der Gleichung ändert. |
Deine neue Lieblings-Merkregel zum Umformen von Termen und Gleichungen:
Rechne immer Klammer vor Punkt vor Strich!
Wende diese Regel nun auf die folgenden Aufgaben an. Beachte immer die Grundmenge, die rechts steht.
Wenn du dir sicher bist, welche Äquivalenzumformung als nächstes kommt, darfst du durch Markieren des grauen Feldes den jeweils nächsten Schritt sichtbar machen!
Erst ganz am Ende kannst du dann dein Ergebnis durch Klick auf "Lösung anzeigen" überprüfen.
- Beispiel :
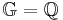
- 3x + 10 = 19
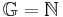
- 3x + 10 = 19 | - 10
 3x = 9 | : 3
3x = 9 | : 3
 x = 3
x = 3
- 9x - 18 = 27
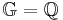
- 9x - 18 = 27 | + 18
 9x = 45 | : 9
9x = 45 | : 9
 x = 5
x = 5
- 12 - 12 : 12 = 2x + 2 : 2
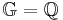
 12 - 1 = 2x + 1 | - 1
12 - 1 = 2x + 1 | - 1
 10 = 2x | : 2
10 = 2x | : 2
 x = 5
x = 5
- 23 + 32 = 5x + 17
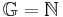
 8 + 9 = 5x + 17
8 + 9 = 5x + 17
 17 = 5x + 17 | - 17
17 = 5x + 17 | - 17
 0 = 5x | : 5
0 = 5x | : 5
 x = 0 ... wirklich?
x = 0 ... wirklich?
- 3x + 8 + 6x - 3 = -13
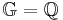
 9x + 5 = -13 | - 5
9x + 5 = -13 | - 5
 9x = -18 | : 9
9x = -18 | : 9
 x = -2
x = -2
- -3
 (3 - 2x) + 2x = -21
(3 - 2x) + 2x = -21
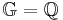
 -9 + 6x + 2x = -21
-9 + 6x + 2x = -21
 -9 + 8x = -21 | + 9
-9 + 8x = -21 | + 9
 8x = -12 | : 8
8x = -12 | : 8
 x = -1,5
x = -1,5

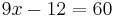
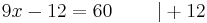
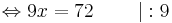
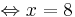

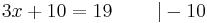
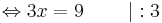
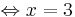

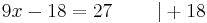
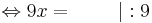
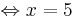

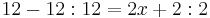
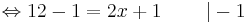
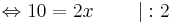
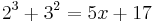
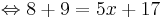
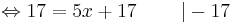
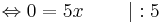
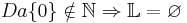
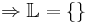
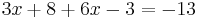
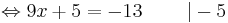
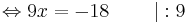
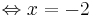
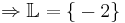
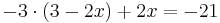
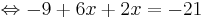
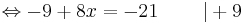
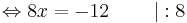
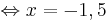
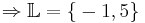
 Weiter zu 7. Klasse Geometrie
Weiter zu 7. Klasse Geometrie Zurück zu 6. Klasse Geometrie
Zurück zu 6. Klasse Geometrie
