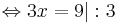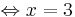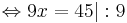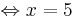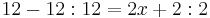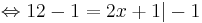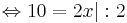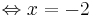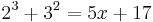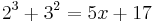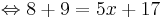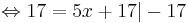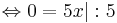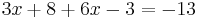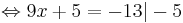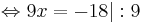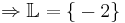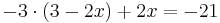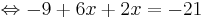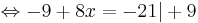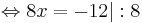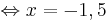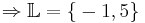Algebra: Terme und Gleichungen: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus DMUW-Wiki
K |
K |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| − | + | '''Deine neue Lieblings-Merkregel:'''<br> | |
<div class="schuettel-quiz"> | <div class="schuettel-quiz"> | ||
Rechne immer '''Klammer''' vor '''Punkt''' vor '''Strich'''! | Rechne immer '''Klammer''' vor '''Punkt''' vor '''Strich'''! | ||
| Zeile 6: | Zeile 6: | ||
| − | ''Wenn du dir sicher bist, welche Äquivalenzumformung als nächstes kommt, darfst du durch Markieren des grauen Feldes den jeweils nächsten Schritt sichtbar machen!Erst ganz am Ende kannst du dann dein Ergebnis durch Klick auf "Lösung anzeigen" überprüfen.'' | + | |
| + | ''Wenn du dir sicher bist, welche Äquivalenzumformung als nächstes kommt, darfst du durch Markieren des grauen Feldes den jeweils nächsten Schritt sichtbar machen!'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Erst ganz am Ende kannst du dann dein Ergebnis durch Klick auf "Lösung anzeigen" überprüfen.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
* 3x + 10 = 19 <u style="color:lightgrey;background:lightgrey"> | - 10 </u> | * 3x + 10 = 19 <u style="color:lightgrey;background:lightgrey"> | - 10 </u> | ||
Version vom 27. Juni 2009, 11:41 Uhr
Deine neue Lieblings-Merkregel:
Rechne immer Klammer vor Punkt vor Strich!
Wenn du dir sicher bist, welche Äquivalenzumformung als nächstes kommt, darfst du durch Markieren des grauen Feldes den jeweils nächsten Schritt sichtbar machen!
Erst ganz am Ende kannst du dann dein Ergebnis durch Klick auf "Lösung anzeigen" überprüfen.
- 3x + 10 = 19 | - 10
 3x = 9 | : 3
3x = 9 | : 3
 x = 3
x = 3
- 9x - 18 = 27 | + 18
 9x = 45 | : 9
9x = 45 | : 9
 x = 5
x = 5
- 12 - 12 : 12 = 2x + 2 : 2
 12 - 1 = 2x + 1 | - 1
12 - 1 = 2x + 1 | - 1
 10 = 2x | : 2
10 = 2x | : 2
 x = 5
x = 5
 8 + 9 = 5x + 17
8 + 9 = 5x + 17
 17 = 5x + 17 | - 17
17 = 5x + 17 | - 17
 0 = 5x | : 5
0 = 5x | : 5
 x = 0
x = 0
- 3x + 8 + 6x - 3 = -13
 9x + 5 = -13 | - 5
9x + 5 = -13 | - 5
 9x = -18 | : 9
9x = -18 | : 9
 x = -2
x = -2
 -9 + 6x + 2x = -21
-9 + 6x + 2x = -21
 -9 + 8x = -21 | + 9
-9 + 8x = -21 | + 9
 8x = -12 | : 8
8x = -12 | : 8
 x = -1,5
x = -1,5