Eigenschaften: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus DMUW-Wiki
(Layoutänderung) |
(link geändert) |
||
| (14 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| + | <div style="margin:0; margin-right:4px; margin-left:0px; border:2px solid #f4f0e4; padding: 0em 0em 0em 1em; background-color:#f4f0e4;">[[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion|Übersicht]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Einleitung|Einleitung]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Zinseszins|Zinseszins]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Untersuchung|Untersuchung der Exponentialfunktion]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Eigenschaften|Eigenschaften der Exponentialfunktion]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Umkehrfunktion|Umkehrfunktion]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Rechnerische Beziehung|Rechnerische Beziehung]] - [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Übungen|Übungen und Lösung des Arbeitsblattes]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
==Eigenschaften der Exponentialfunktion== | ==Eigenschaften der Exponentialfunktion== | ||
| + | {| {{Prettytable}} | ||
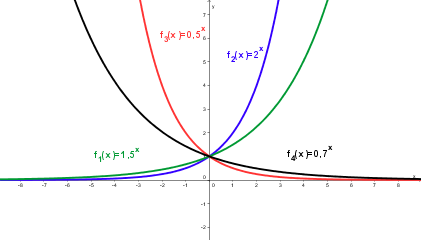
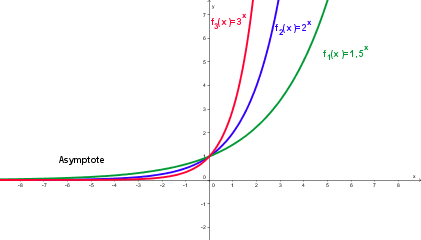
| + | |'''Die Definitionsmenge aller Exponentialfunktionen ist R. Es treten nur positve Funktionswerte auf. Alle Exponentialfunktionen der Form f(x) = a<sup>x</sup> gehen durch den Punkt (0/1).''' || [[Bild:Exponentialfunktionen.png]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
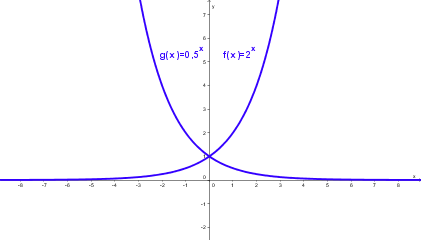
| + | | [[Bild:Exponentialfunktion7.png]] || '''Die Graphen von f(x) = a<sup>x</sup> und g(x) = a<sup>-x</sup> = 1/a<sup>x</sup> liegen symmetrisch bezüglich der y-Achse.''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
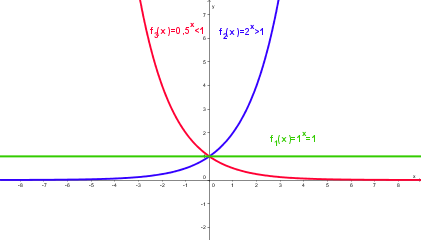
| + | | '''<span style="color:#ff0000">Für 0 < a < 1 ist die Exponentialfunktion monoton fallend</span>, <span style="color:#008B00">für a = 1 ist die Funktion konstant</span>, <span style="color:#00008B">für a > 1 ist sie monoton steigend.</span>''' || [[Bild:Exponentialfunktion2.png]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
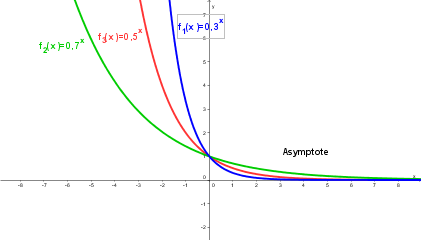
| + | |[[Bild:Exponentialfunktion6.png]] || '''Für 0 < a < 1 ist die positive x-Achse Asymptote.''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Für a > 1 ist die negative x-Achse Asymptote.''' || [[Bild:Exponentialfunktion5.png]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {{Merksatz|MERK= | ||
| + | * Die Definitionsmenge aller Exponentialfunktionen ist R. | ||
| + | * Es treten nur positive Funktionswerte auf. | ||
| + | * Alle Exponentialfunktionen der Form f(x) = a<sup>x</sup> gehen durch den Punkt (0/1). | ||
| + | * Die Graphen von f(x) = a<sup>x</sup> und g(x) = a<sup>-x</sup> = 1/a<sup>x</sup> liegen symmetrisch bezüglich der y-Achse. | ||
| + | * Für 0 < a < 1 ist die Exponentialfunktion monoton fallend, für a = 1 ist die Funktion konstant, für a > 1 ist sie monoton steigend. | ||
| + | * für 0 < a < 1 ist die positive x-Achse Asymptote. | ||
| + | * Für a > 1 ist die negative x-Achse Asymptote.}} | ||
| − | + | '''''Löse an dieser Stelle das Arbeitsblatt zum Lernpfad''''' | |
| − | |||
| − | + | → [[Lernpfade/Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktion/Umkehrfunktion|Hier geht´s zur Umkehrfunktion]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 28. Januar 2010, 12:30 Uhr
Übersicht - Einleitung - Zinseszins - Untersuchung der Exponentialfunktion - Eigenschaften der Exponentialfunktion - Umkehrfunktion - Rechnerische Beziehung - Übungen und Lösung des Arbeitsblattes
Eigenschaften der Exponentialfunktion
|
Merke:
|
Löse an dieser Stelle das Arbeitsblatt zum Lernpfad